9 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Introduction
Vitamin B6, also referred to as pyridoxine, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. It belongs to the B-complex group of vitamins, which are necessary for the generation of energy and the breakdown of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Vitamin B6 is particularly significant for the development and functioning of the brain, as it supports the synthesis of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which regulate mood and cognitive functions. Additionally, it aids in the production of hemoglobin, thereby contributing to the transportation of oxygen in the bloodstream.
Despite its significance, vitamin B6 deficiency is relatively common, especially among individuals with poor dietary habits, certain medical conditions, or those taking medications that disrupt B6 metabolism. Potential causes of deficiency include chronic alcoholism, kidney disease, malabsorption syndromes, and the use of specific medications such as anticonvulsants and oral contraceptives. This article explores the nine primary signs and symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency, offering insights into how this deficiency can manifest and impact overall health.
1. Skin Rashes
A clear indication of not getting enough vitamin B6 is the appearance of skin rashes, like seborrheic dermatitis. This issue typically shows up as skin that is scaly, oily, and flaky, mainly on the face, neck, scalp, and upper chest. The rash can cause itching and redness, causing a lot of discomfort.
Vitamin B6 plays a key role in keeping the skin healthy because it helps in making collagen, a protein that’s important for the skin’s firmness and flexibility. Without enough B6, the skin’s ability to heal and renew itself decreases, leading to the formation of rashes and other skin problems. B6 deficiency can also cause seborrheic dermatitis by messing with how the skin processes fats and by weakening the immune system.
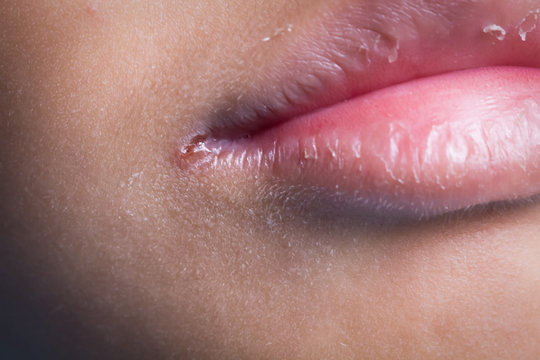
2. Cracked and Sore Lips
A prominent indicator of vitamin B6 insufficiency is cheilosis, a condition distinguished by chapped and painful lips, especially at the edges of the mouth. This can lead to significant discomfort and hinder activities such as eating, drinking, and speaking. The skin at the corners of the mouth may become swollen, red, and vulnerable to infections.
Vitamin B6 is a critical factor in maintaining the health and integrity of the skin, particularly the delicate skin around the lips. It aids in the production of collagen and supports the immune system, which helps prevent infections that can exacerbate skin problems. A lack of B6 can compromise the skin’s protective function, making it more susceptible to cracking and inflammation. Additionally, vitamin B6 is involved in the metabolism of proteins and fats, which are essential for maintaining healthy skin cells and preventing conditions like cheilosis.
3. Sore, Glossy Tongue
Glossitis, a painful and shiny tongue, is another symptom of vitamin B6 deficiency. Glossitis can cause significant discomfort, making it difficult to eat, drink, and speak. The tongue may appear swollen, red, and smooth, lacking the typical rough texture due to the atrophy of papillae, the small bumps on the tongue’s surface.
Vitamin B6 is crucial for maintaining the health of mucous membranes, including those in the mouth. It plays a role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and hemoglobin, both of which are essential for the health and function of the tongue’s muscles and tissues. A deficiency in B6 can lead to inflammation and degeneration of these tissues, resulting in symptoms such as glossitis. Additionally, B6 deficiency can impair the body’s ability to repair and regenerate cells, further contributing to the development of a sore and glossy tongue.
4. Mood Changes
Vitamin B6 deficiency has a significant impact on mood, resulting in changes such as irritability, depression, and anxiety. This is due to the essential role of B6 in the production of neurotransmitters, which are responsible for regulating mood and cognitive function. Serotonin, dopamine, and GABA are three key neurotransmitters that are particularly affected by the availability of B6.
Serotonin is known as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness. Dopamine is crucial for motivation and reward, while GABA acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps to calm the nervous system. When there is a deficiency in vitamin B6, the synthesis of these neurotransmitters is disrupted, leading to imbalances that impact mood regulation. As a result, individuals with low levels of B6 may experience heightened levels of stress, anxiety, depression, and irritability.
5. Weakened Immune Function
Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in maintaining a strong immune system. Insufficient levels of this vitamin can result in a compromised immune function, leaving individuals more vulnerable to infections and diseases. B6 is essential for the development and operation of white blood cells, which are vital for detecting and fighting off pathogens.
Additionally, vitamin B6 is responsible for the production of antibodies, which are proteins that target and deactivate harmful invaders. It also contributes to the regulation of inflammation and the prevention of chronic inflammatory conditions. A deficiency in B6 can hinder these immune functions, increasing the likelihood of infections and reducing the body’s ability to recover from illnesses.
6. Tiredness and Low Energy
Vitamin B6 deficiency commonly manifests as chronic fatigue and low energy levels due to its involvement in various metabolic processes that are essential for energy production. Specifically, B6 plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, converting these macronutrients into usable energy for the body.
Moreover, Vitamin B6 is vital for the synthesis of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to different parts of the body within red blood cells. Inadequate levels of B6 can hinder hemoglobin production, resulting in microcytic anemia characterized by smaller and less efficient red blood cells. Consequently, individuals may experience symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and decreased energy levels.
7. Tingling and Numbness
Vitamin B6 deficiency can result in peripheral neuropathy, which is characterized by tingling and numbness in the hands and feet. This condition arises due to the crucial role of B6 in maintaining nerve health and function. Vitamin B6 is essential for the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the formation of myelin, the protective covering around nerves that facilitates efficient transmission of nerve signals.
Insufficient levels of vitamin B6 can lead to damage to the myelin sheath, resulting in nerve dysfunction and the development of peripheral neuropathy symptoms. These symptoms may manifest as a feeling of pins and needles, numbness, and even pain in the extremities. If left untreated, peripheral neuropathy can progress and cause significant impairment in both sensation and motor function.
8. Cognitive Disturbances
Vitamin B6 deficiency may result in cognitive impairments, such as memory issues and disorientation. B6 is vital for brain function, as it aids in the creation of neurotransmitters crucial for cognitive functions. Serotonin, dopamine, and GABA are all involved in regulating mood, forming memories, and overall cognitive performance.
Insufficient B6 levels can disrupt the balance of these neurotransmitters, causing symptoms like disorientation, memory lapses, and trouble focusing. Additionally, B6 is essential for hemoglobin production, which is needed to transport oxygen to the brain. Inadequate oxygen supply to the brain can hinder cognitive function, leading to cognitive impairments. In severe instances, prolonged B6 deficiency can contribute to the onset of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
9. Anemia
Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a deficiency of healthy red blood cells, resulting in symptoms like tiredness, paleness, and difficulty breathing. A specific form of anemia linked to a lack of vitamin B6 is microcytic anemia, where red blood cells are smaller than usual and less effective at carrying oxygen.
Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in the production of hemoglobin, the protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for transporting oxygen. Inadequate levels of B6 can hinder hemoglobin synthesis, leading to the onset of anemia. This can manifest in symptoms such as persistent fatigue, weakness, and paleness. Furthermore, anemia can worsen other signs of vitamin B6 deficiency, including cognitive issues and low energy levels.
A Quick Review
Vitamin B6 plays a vital role in supporting various physiological functions within the body, such as skin health, mood regulation, immune response, energy metabolism, nerve function, cognitive abilities, and hemoglobin synthesis. A deficiency in this essential nutrient can manifest through a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from skin issues and inflamed lips to alterations in mood, compromised immunity, and anemia.
Maintaining a well-rounded diet that incorporates B6-rich foods like poultry, fish, potatoes, chickpeas, bananas, and fortified cereals is crucial in preventing a deficiency of this vitamin. In certain circumstances, supplementation may be required, especially for individuals with underlying medical conditions or those on medications that hinder B6 absorption.
Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals is imperative in the identification and management of vitamin B6 deficiency. They can provide tailored advice on dietary modifications, supplementation, and other strategies to ensure optimal B6 levels and overall well-being.